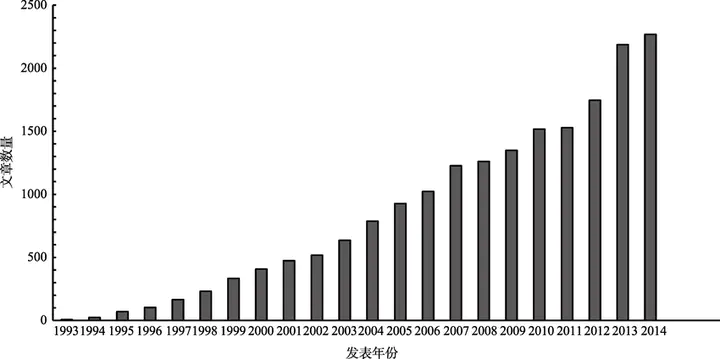
 Image credit: Fig1
Image credit: Fig1
Abstract
With increasing popularity of high resolution neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and position emission computerized tomography (PET), a large number of neuroimaging studies have been accumulated in the last two decades.These new data brought both opportunities and challenges for cognitive neuroscientists,enabling them to generate and examine new hypotheses. Given the main goal of neuroimaging is to explore the relationship between cognitive processes and corresponding locations in brain, coordinate-based meta-analysis become the dominant method for neuroimaging data. One such method, activation likelihood estimation (ALE), is the most widely used, because of its methodological superiority and usability. The current review first introduced basic principles of ALE method. Next, the two most common approaches of conducting meta-analysis of neuroimaging data were discussed:finding consistency across studies and finding modulators of brain activations. Furthermore, the newly emerged meta-analytic connectivity modeling (MACM), which used the meta-analysis to explore the functional connectivity of the brain, was illustrated using recent studies. Finally, the current review discussed several directions in the field of meta-analysis of neuroimaging data.